Biodegradable Plastics: The Future of Sustainable Packaging
Imagine a world where packaging doesn’t contribute to the growing mountains of waste in our landfills and oceans. Instead, it breaks down naturally, returning to the earth without leaving a trace. This isn’t just a dream but a rapidly approaching reality thanks to the latest advancements in biodegradable plastics. The global biodegradable plastics market was valued at approximately $5.28 billion and is expected to grow up to 3 folds by 2030, to $14.43 billion. These innovative materials hold the promise of revolutionizing packaging, significantly reducing our environmental footprint. Read on to discover how biodegradable plastics are set to transform our world for the better.
What are Biodegradable Plastics?
Biodegradable plastics are designed to decompose naturally through the action of living organisms, such as bacteria and fungi. Unlike traditional plastics, which can take hundreds of years to break down, biodegradable plastics can degrade in a matter of months under the right conditions. This attribute makes them an exciting alternative in the fight against plastic pollution.
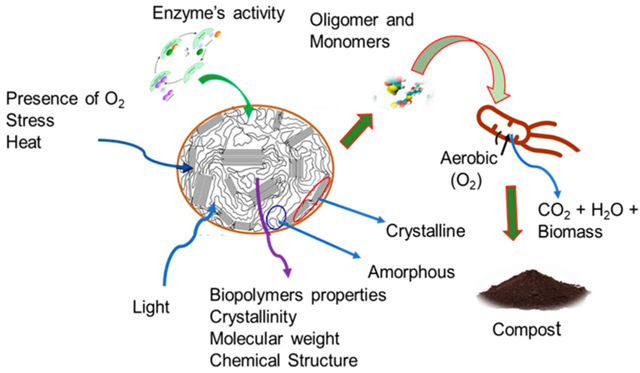
The Science Behind Biodegradable Plastics
Biodegradable plastics are made from various natural sources, including plants, starches, and other renewable materials. The most common types include:
- Polylactic Acid (PLA): Derived from fermented plant starch (usually corn), PLA is widely used in food packaging and disposable tableware.
- Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA): Produced by bacterial fermentation of sugars or lipids, PHA is versatile and can be used in a variety of applications, from medical devices to packaging.
- Starch Blends: These are created by blending starch with other biodegradable polymers to enhance their properties and usability.
The decomposition process involves microorganisms breaking down the plastic into water, carbon dioxide, and biomass, which can then be absorbed by the environment. This biodegradation can occur in industrial composting facilities or, in some cases, even in home compost setups.
Advantages of Biodegradable Plastics
Biodegradable plastics offer several significant benefits over traditional plastics:
- Reduced Environmental Impact: One of the most compelling advantages is their ability to break down quickly, reducing the volume of waste in landfills and oceans.
- Lower Carbon Footprint: The production of biodegradable plastics typically generates fewer greenhouse gases compared to conventional plastics, contributing to a decrease in overall carbon emissions.
- Sustainable Sourcing: Many biodegradable plastics are made from renewable resources, lessening our reliance on fossil fuels and promoting agricultural industries.
- Versatility: Biodegradable plastics can be engineered to meet a wide range of applications, from packaging to medical uses, making them a flexible solution for many industries.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their promise, biodegradable plastics face several challenges:
- Cost: Currently, biodegradable plastics are more expensive to produce than traditional plastics. However, as technology advances and production scales up, costs are expected to decrease.
- Infrastructure: Effective biodegradation often requires specific conditions found in industrial composting facilities. The lack of such infrastructure in many areas can limit the effectiveness of biodegradable plastics.
- Public Awareness: Consumers need better education on how to properly dispose of biodegradable plastics to ensure they are composted and not mistakenly recycled with traditional plastics.
Innovations Driving the Future
Recent advancements in biodegradable plastic technology are addressing some of these challenges and opening new possibilities:
- Enhanced Degradation Rates: Researchers are developing new formulations that break down more quickly and efficiently, even in less-than-ideal conditions.
- Improved Performance: Innovations are leading to biodegradable plastics that match or exceed the strength and durability of conventional plastics, broadening their application range.
- Eco-Friendly Additives: Scientists are exploring natural additives that can enhance biodegradability and performance without adding significant cost.
The Role of Biodegradable Plastics in Packaging
Packaging is one of the largest uses of plastic globally, making it a prime target for biodegradable alternatives. From food containers to shipping materials, biodegradable plastics can drastically reduce the environmental impact of packaging. Here are some specific areas where they are making a difference:
- Food Packaging: Biodegradable plastics can safely encase food items, reducing waste and promoting compostable packaging solutions.
- Single-Use Items: Items like straws, cutlery, and plates, often used once and discarded, are prime candidates for biodegradable plastic alternatives.
- Shipping Materials: Biodegradable plastics can replace traditional bubble wrap, packing peanuts, and other shipping materials, ensuring that packaging waste does not contribute to long-term pollution.

Policies and Trends Across the Globe
Governments and industries worldwide are increasingly recognizing the potential of biodegradable plastics and are enacting policies and trends to support their adoption:
USA: In the United States, several states, including California and New York, have implemented bans on single-use plastics and are promoting the use of biodegradable alternatives. Federal initiatives, like the Break Free from Plastic Pollution Act, aim to reduce plastic waste and encourage sustainable packaging solutions.
Europe: The European Union has been a leader in environmental policy, with the European Commission’s Plastics Strategy aiming for all plastic packaging to be recyclable or reusable by 2030. The EU has also implemented directives to reduce single-use plastics, boosting demand for biodegradable options.
Asia: In Asia, countries like China, Japan, etc. are ramping up their efforts to tackle plastic pollution. China has introduced ambitious policies to reduce plastic waste, including banning non-degradable bags and promoting biodegradable materials.
Africa: Several African nations are taking proactive steps to address plastic waste. Rwanda and Kenya have implemented some of the world’s strictest plastic bag bans, and South Africa is exploring biodegradable packaging to reduce its plastic footprint. These policies are driving innovation and adoption of biodegradable plastics across the continent.
Conclusion
Biodegradable plastics represent a promising solution to one of the most pressing environmental issues of our time: plastic pollution. By embracing these innovative materials, we can significantly reduce our environmental impact, promote sustainability, and move towards a greener future. As advancements continue and adoption grows, biodegradable plastics have the potential to revolutionize the packaging industry and beyond, making our world a cleaner, healthier place for generations to come.
Embrace the change, support sustainable practices, and let’s work together to build a future where our packaging leaves no trace behind.

0 Comments