Superhydrophobic Materials: Water-Repellent Surfaces and Applications
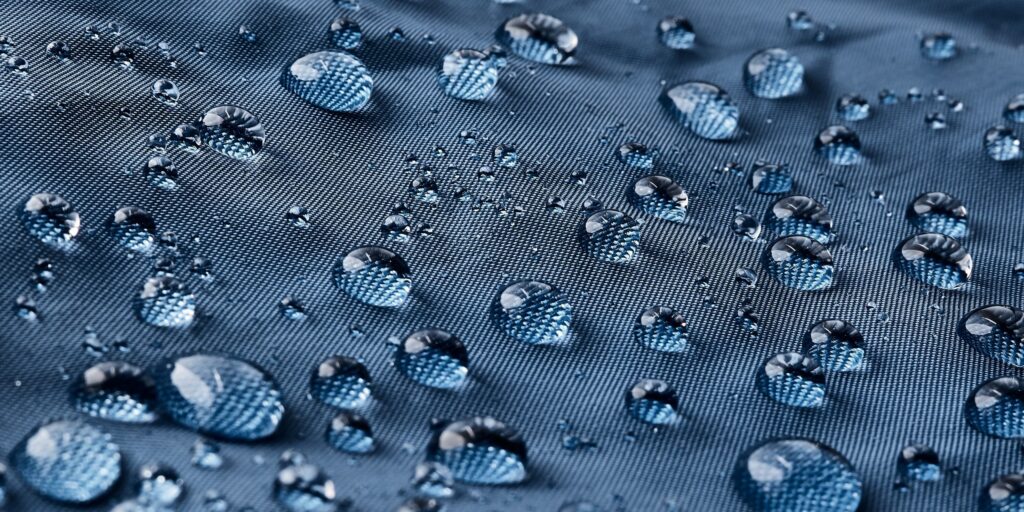

Superhydrophobic materials have garnered significant attention in recent years due to their remarkable ability to repel water. Inspired by nature’s design, these surfaces exhibit extraordinary water-repellent properties, finding applications across various industries. This article delves into the fascinating world of superhydrophobic materials, exploring their characteristics, fabrication methods, and diverse applications, ranging from self-cleaning surfaces to preventing ice formation on critical structures.
What is Superhydrophobicity?
Superhydrophobicity refers to the extreme water repellency of certain materials, mimicking the water-shedding abilities observed in natural phenomena like lotus leaves. The key to superhydrophobicity lies in the surface micro- and nanostructures that trap air, minimizing contact with water droplets. Common materials known for their superhydrophobic properties include silicones, fluoropolymers, and nanoparticles.
How Superhydrophobicity Can Be Attained?
Several techniques are employed to create superhydrophobic surfaces, such as chemical modification, electrospinning, and microfabrication. Chemical methods involve applying hydrophobic coatings or modifying the surface chemistry to induce water-repellent characteristics. Micro- and nanostructuring, achieved through laser ablation or etching processes, is another effective approach. These fabrication methods contribute to the development of durable and efficient superhydrophobic materials.
What are the Applications of Superhydrophobic Materials?
- Self-Cleaning Surfaces: Superhydrophobic materials find extensive use in self-cleaning applications. The water-repellent surfaces prevent the adhesion of dirt, pollutants, and biological matter, allowing rain or water to wash away contaminants easily. This property is harnessed in architectural coatings, car paints, and outdoor textiles, reducing maintenance efforts and enhancing the longevity of surfaces.
- Anti-Icing Technologies: In cold climates, ice formation on surfaces poses significant challenges. Superhydrophobic materials offer a solution by preventing ice accumulation. These surfaces minimize the contact area between ice and the substrate, making it difficult for ice to adhere. Applications include aircraft wings, power lines, and wind turbine blades, where the prevention of ice formation is crucial for operational efficiency and safety.
- Water-Repellent Electronics: Superhydrophobic coatings are applied to electronic devices to protect them from water damage. This is especially valuable in outdoor or industrial settings where electronic equipment is exposed to environmental elements. Water-repellent electronics contribute to increased device reliability and lifespan.
- Medical Devices: Superhydrophobic materials have promising applications in the medical field. For example, they can be used to create water-resistant and self-cleaning surfaces for medical implants or devices, reducing the risk of infections and enhancing biocompatibility.
- Oil-Water Separation: The ability of superhydrophobic materials to repel water while selectively attracting oil makes them valuable in oil-water separation processes. These materials can be utilized in filters and membranes to efficiently separate oil and water in industrial and environmental remediation applications.
Conclusion
Superhydrophobic materials represent a groundbreaking advancement in material science, offering various applications that span various industries. From self-cleaning surfaces to preventing ice formation on critical structures, the versatility of these materials continues to drive innovation and address challenges associated with water interactions. As research in this field progresses, we can expect even more tailored applications and enhanced performance from superhydrophobic materials, contributing to a more sustainable and technologically advanced future.


0 Comments